Home » Concepts » Discrimination & Harassment » Causal connection
A causal connection is a legal term that refers to the link between a person’s action and a resulting outcome. In employment law, establishing a causal connection is critical when determining whether an adverse employment action—such as termination, demotion, or harassment—was the result of discrimination, retaliation, or another protected activity. Simply put, it helps determine whether the employee’s protected status or conduct directly influenced the employer’s decision or behavior.
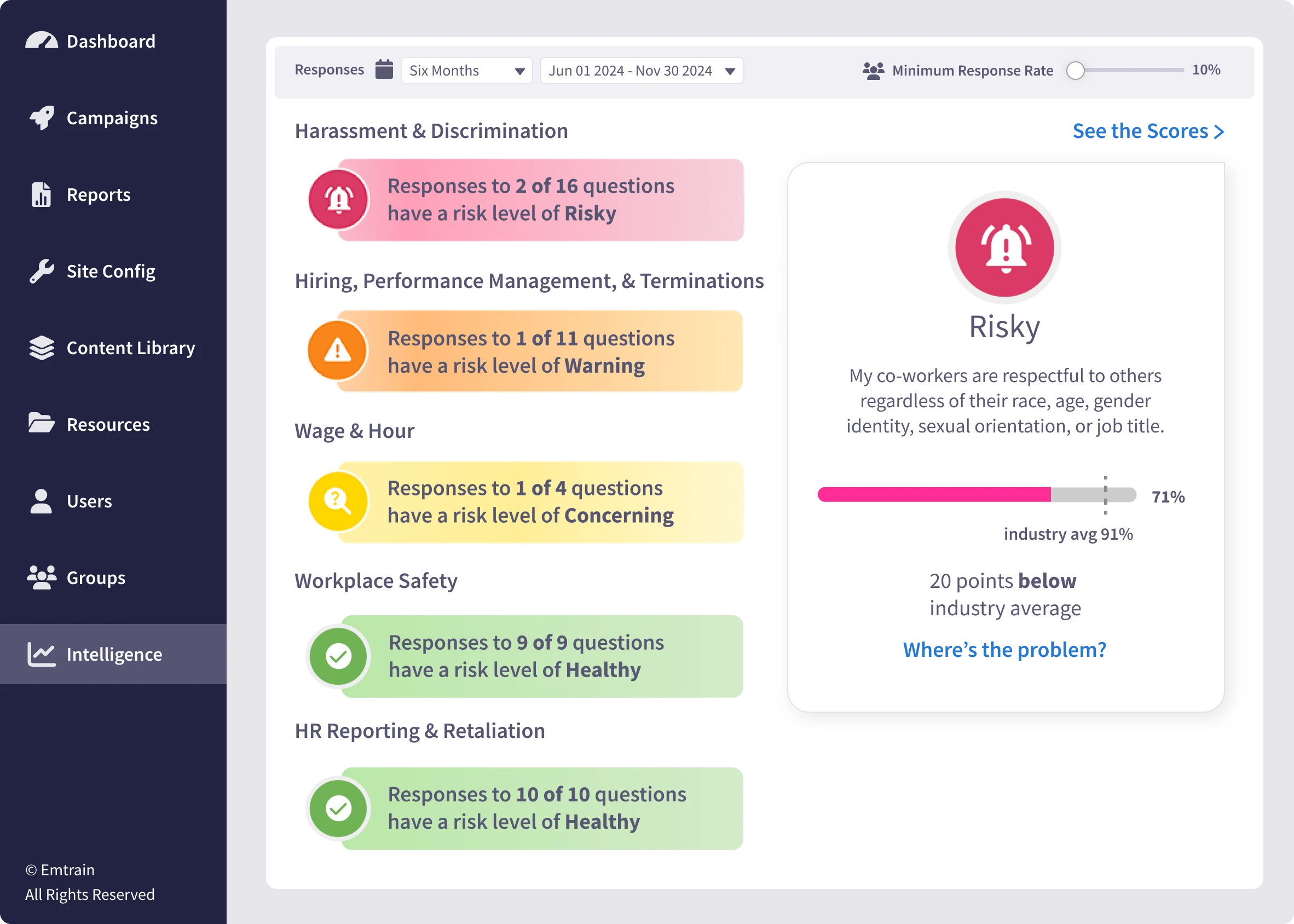
Emtrain’s harassment training course is engaging, interactive, and designed to spot and reduce EEO risk.
In workplace discrimination cases, a causal connection shows that the adverse action taken against an employee (such as firing or denial of promotion) was directly related to a protected characteristic or activity—like race, gender, disability, or filing a harassment complaint. It’s a core component in establishing liability in both internal investigations and legal proceedings.
To prove a causal connection, the employee must present evidence that links the protected activity or characteristic to the adverse action. This may include:
Employers must be able to demonstrate legitimate, non-discriminatory reasons for their decisions to avoid legal exposure.
For investigators and HR professionals, understanding causal connection is critical to assessing:
Establishing or ruling out a causal link helps determine whether misconduct occurred and informs appropriate remediation.
Causal connection is one of the legal standards used in:
Courts assess whether the protected activity was a “motivating factor” or “but-for cause” in the adverse employment action. Without a clear causal connection, claims are unlikely to succeed.
These courses help learners understand how causal connection applies in real-world workplace scenarios:
Emtrain’s workplace training content helps employees and managers:
Emtrain’s video-based training shows realistic scenarios that demonstrate how a causal connection might be inferred—or ruled out—based on the facts.
Age Bias Salary & Responsibility Shift
An older employee is denied a raise and stripped of responsibilities. The manager cites a desire to make room for others and hints the employee should retire. This clear instance of age-based intent provides a vivid example of causal connection under the ADEA.