Home » Concepts » Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion » Prejudice
Prejudice refers to preconceived opinions or attitudes about individuals or groups that are not based on reason or actual experience. These attitudes can lead to discriminatory behavior and perpetuate biases in workplaces, schools, and society. Prejudices can stem from cultural, social, or personal beliefs and often manifest in ways that harm workplace dynamics and hinder inclusion.
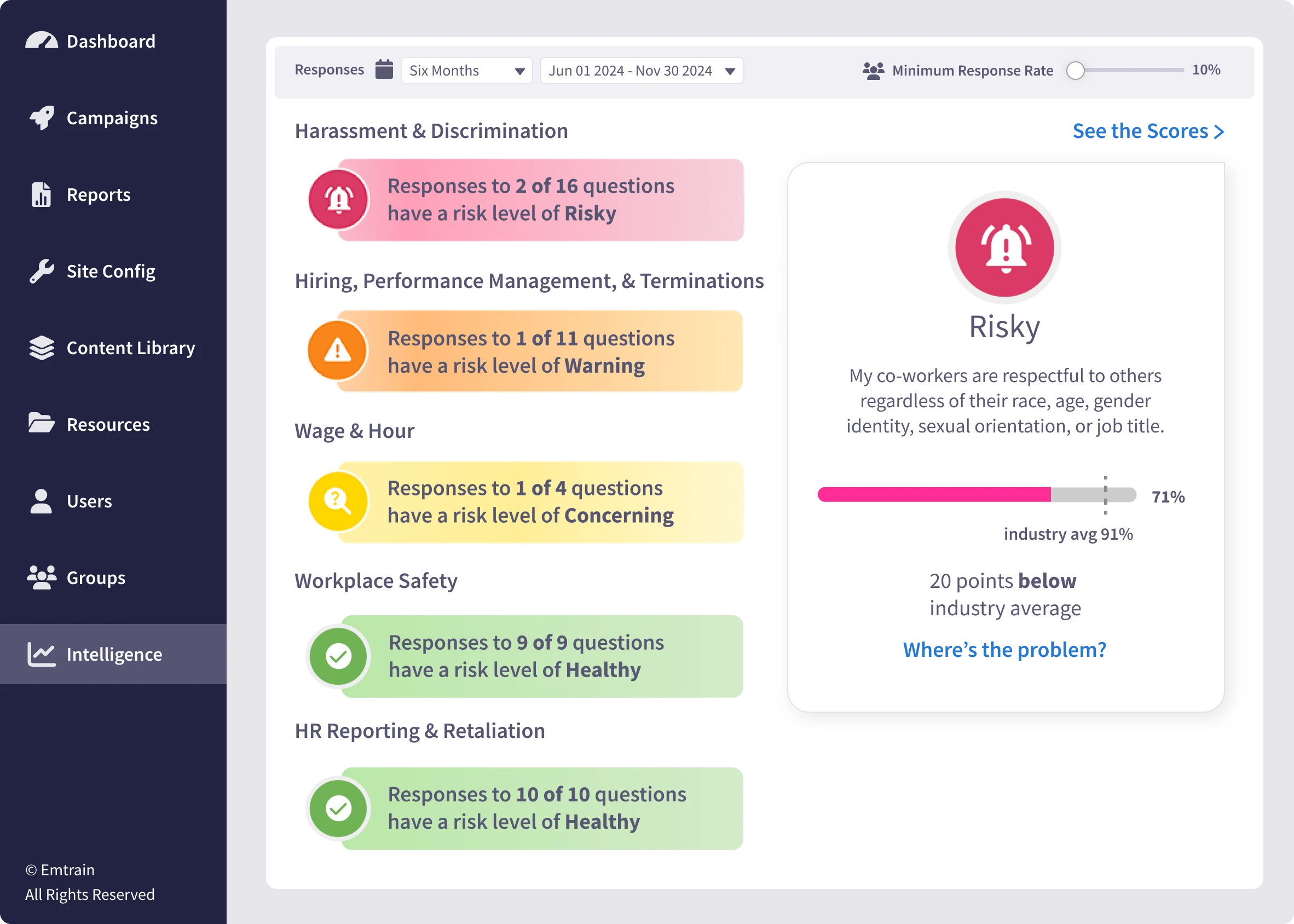
Emtrain’s harassment training course is engaging, interactive, and designed to spot and reduce EEO risk.
Prejudice has shaped societal structures and workplace policies for centuries, often creating barriers for marginalized groups. From the civil rights movements of the 20th century to the ongoing fight for equality in the workplace, prejudice has been a significant obstacle to progress.
Workplace prejudice became a focal point in the late 1900s with the introduction of Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) laws aimed at dismantling discriminatory practices in hiring, promotion, and team dynamics. Despite legislative progress, unconscious biases and systemic prejudice still persist, impacting workplace cultures globally.
These scenarios highlight the importance of addressing prejudice to build equitable, inclusive workplaces.
Addressing prejudice requires awareness, intentionality, and organizational commitment to inclusivity.
By addressing prejudice head-on, workplaces can foster environments that celebrate diversity and collaboration.
Proactive Measures:
Real-World True Stories of Diversity and Bias
Read real-life examples of how diversity challenges arise and strategies to address them effectively.
Microaggressions, like assuming someone’s first-generation status, can unintentionally communicate bias or discrimination. This video explores how such assumptions can negatively impact workplace dynamics and offers actionable steps to foster inclusivity and understanding.
Key Takeaway: Recognizing and addressing microaggressions creates a culture where every individual feels seen and respected.